Understanding the Different Types of 3D Filaments and Their Uses
3D printing has taken the world by storm, transforming how we think about manufacturing, prototyping, and even art! At the heart of this fascinating technology is something quite simple but essential—the filament. Just like a pencil needs lead to draw, a 3D printer relies on different types of filaments to create everything from prototypes to custom toys. If you’ve ever been curious about what goes into your 3D-printing projects, you’re in the right place. Let’s dive into the world of 3D filaments and explore the unique properties and common applications of various types.
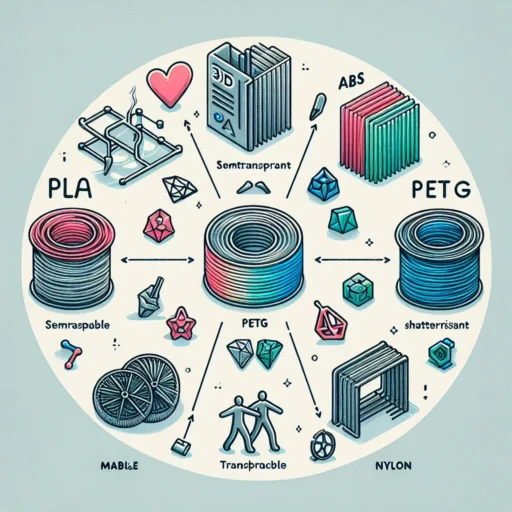
PLA (Polylactic Acid)
One of the most popular types of 3D filament, PLA is biodegradable and made from renewable resources like cornstarch or sugarcane. This environmentally-friendly option is fantastic for beginners due to its ease of use. It prints at lower temperatures, around 180-220°C, and adheres well to many surfaces.
Uses
PLA is a go-to for basic printing projects, including figurines, prototypes, and even some educational models. However, it’s not the most durable choice—so if you need something that will withstand heat or stress, you might want to consider alternatives.
ABS (Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene)
If you’re searching for strength and durability, ABS is a fantastic choice. This filament can handle higher temperatures (printing around 210-250°C) and results in a sturdier final product compared to PLA. It’s also resistant to impact, making it ideal for functional parts.
Uses
ABS is often used for creating mechanical parts, automotive components, and toys (think LEGO bricks!). However, working with ABS can come with challenges, including warping and unpleasant fumes during printing, so proper ventilation is crucial.
PETG (Polyethylene Terephthalate Glycol)
Continuing the trend for durable materials, PETG is a popular choice that combines the best of both worlds—ease of printing and strength. It’s less brittle than ABS and more heat-resistant than PLA, printing at temperatures ranging from 220°C to 250°C.
Uses
Because PETG has excellent clarity and is often food-safe, it’s great for making containers, medical supplies, and even electrical enclosures. It provides good layer adhesion and is less prone to warping, making it a favorite among 3D printing enthusiasts.
TPU (Thermoplastic Polyurethane)
If you’re looking for flexibility, TPU is your go-to. This filament is rubber-like, allowing for tremendous elasticity and durability. Printing with TPU requires a well-tuned 3D printer, as it’s more challenging to work with than rigid filaments—typically requiring slower print speeds.
Uses
TPU is perfect for producing flexible parts such as phone cases, wearables, and toys. Its resistance to abrasion and impact makes it ideal for custom grips and durable components that require a bit of stretch.
Nylon
Nylon is a robust, versatile filament that’s well-known for its strength and flexibility. It’s a bit more complicated to print due to its strong tendency to absorb moisture from the air, but the resulting objects are incredibly durable and resilient, even at higher temperatures.
Uses
Nylon is commonly used for functional parts such as gears, mechanical components, and durable tools. If you require items that need to endure wear and tear, nylon is definitely worth considering.
ASA (Acrylonitrile Styrene Acrylate)
Similar to ABS, ASA filaments embody many of the same properties but with improved UV resistance and weather resistance. If you’re thinking of outdoor projects, ASA is a fantastic option given its ability to withstand the elements without degrading over time.
Uses
ASA is an excellent choice for outdoor equipment, signage, and automotive parts. If you want durability combined with aesthetic appeal, ASA might just be the perfect balance you’re after.
Specialty Filaments: The Creative Possibilities
Beyond these common types, there are numerous specialty filaments infused with various materials like wood, metal, and glow-in-the-dark materials. These options allow creators to explore their artistic side, crafting unique and one-of-a-kind pieces.
Wrap Up
Navigating the world of 3D filaments is a journey of discovery, as each type offers distinct properties and potential applications. Whether you’re a hobbyist, a professional, or someone simply intrigued by technology, understanding these options empowers you to choose the right filament for your projects. As the 3D printing landscape continues to evolve, the possibilities are virtually endless, limited only by your creativity and imagination. So go ahead, experiment with different filaments, and let your ideas come to life!