3D Printing Technologies Explained: FDM vs. SLA vs. SLS
3D printing has taken the world by storm, revolutionizing everything from manufacturing to healthcare, and even art. If you’ve ever thought about diving into this exciting realm, you may have stumbled upon some acronyms that sound like secret codes: FDM, SLA, and SLS. But worry not, because today we’re going to demystify these terms and discuss what sets them apart.
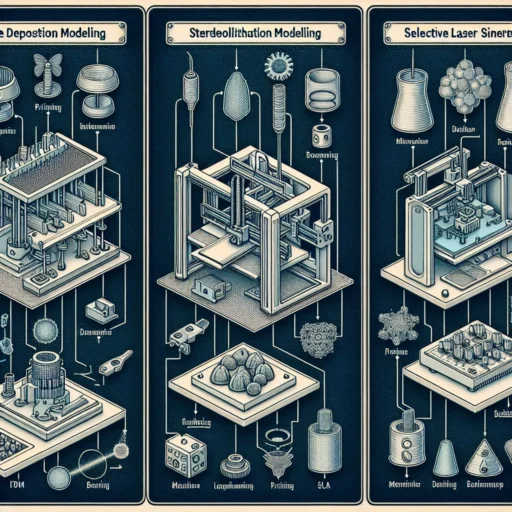
FDM: Fused Deposition Modeling
Let’s kick things off with one of the most popular and widely-used methods: Fused Deposition Modeling (FDM). You might have heard FDM referred to as the granddaddy of 3D printing, and for good reason! This method works by melting thermoplastic filament and extruding it through a heated nozzle layer by layer. It’s like a hot glue gun but way cooler.
Materials & Colors: FDM printers can use a variety of filament materials, such as PLA, ABS, PETG, and more, in an explosion of colors. This gives you tons of options for your prints, whether you’re creating prototypes or fun models.
Speed & Cost: FDM printers are often more affordable and widely available, making them a great choice for hobbyists and educational institutions. Plus, they tend to print fairly quickly compared to some of the other methods. You can have a simple object ready in a couple of hours, depending on your design!
Uses: This technology is perfect for prototyping and producing functional parts. Just think of all those nifty gadgets you could create for your home. Want a phone stand? You got it. How about a customized cookie cutter? Easy peasy!
However, FDM isn’t without its drawbacks. Layer lines can be quite visible, and it might struggle with intricate designs. If you’re after a smooth surface finish or extremely detailed prints, you might want to consider the next options.
SLA: Stereolithography
Next up, we have Stereolithography (SLA). If FDM is the friendly and approachable option, SLA is its more sophisticated sibling. SLA uses a process called photopolymerization, which means it utilizes ultraviolet (UV) light to cure a liquid resin layer by layer. Picture it like crafting a delicate sculpture in a pool of gel.
Materials & Quality: SLA can produce incredibly detailed prints with smooth surfaces, making it the go-to option for professionals needing precision, such as jewelers and dentists. The variety of resin available also allows for different properties, including flexible, hard, or even transparent materials.
Speed & Cost: While SLA prints might take longer than FDM depending on the complexity of the model, the result is often worth the wait. However, the costs can be higher due to the price of the resin and the complexity of the equipment.
Uses: You’ll often see SLA in industries like dentistry for creating custom aligners and crowns, as well as in prototyping and model making. If you’re aiming for high-quality, intricate designs, SLA could be your best friend.
However, keep in mind that SLA resin can be sensitive to light and requires careful handling. You’ll also need some post-processing, like rinsing in isopropyl alcohol (IPA) and curing under UV light, which adds a layer of complexity to the process.
SLS: Selective Laser Sintering
Finally, let’s talk about Selective Laser Sintering (SLS). This technology takes 3D printing to another level by selectively fusing powdered material using a laser. Picture a laser-focused snowstorm in a heated chamber where the particles magically stick together to form a solid object.
Materials & Strength: SLS offers a wide range of materials, from nylon powders to metals, which means it can create strong and functional parts that are ready for industrial use. The final products often boast excellent mechanical properties, making them ideal for end-use applications.
Speed & Cost: SLS can be faster than both FDM and SLA when it comes to batch printing, enabling the production of multiple items in a single print. However, the machines themselves tend to be on the pricier side, catering more to commercial and professional users.
Uses: Industries utilizing SLS technology include aerospace, automotive, and even fashion. With the ability to create complex geometries and lightweight structures, it opens up a whole new world of design possibilities.
While SLS printers are incredibly powerful, they do usually require more oversight and understanding of the materials and processes involved.
Final Thoughts
As you can see, choosing between FDM, SLA, and SLS depends largely on your specific needs and priorities. Whether you’re a hobbyist looking to create fun little gadgets, a professional needing precise objects, or a manufacturer in search of robust parts, each technology offers its own set of advantages and challenges.
In this constantly evolving field, it’s exciting to think about how these technologies will continue to shape industries and our day-to-day lives. So, whichever method strikes your fancy, feel free to dive in and explore the amazing world of 3D printing! Happy printing!