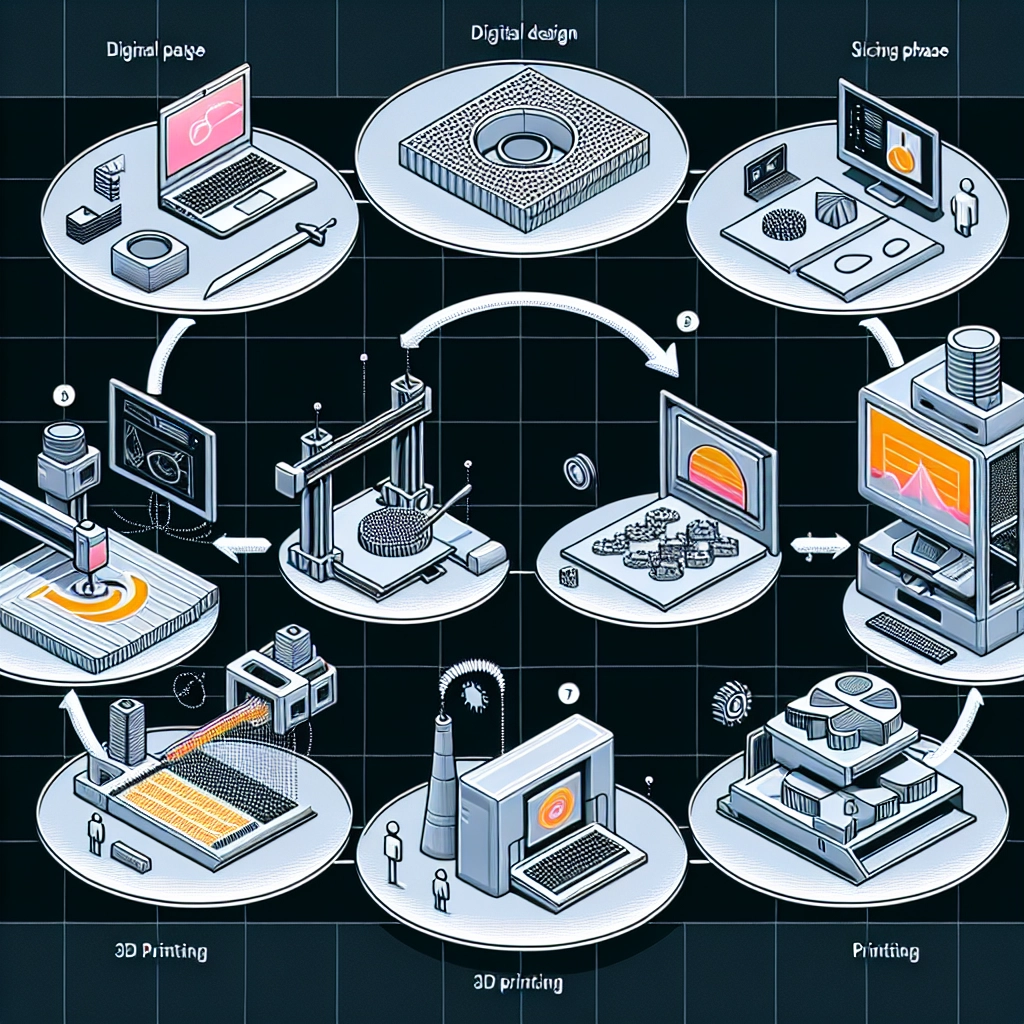
Understanding the 3D Printing Process: From Design to Creation
If you’ve ever marveled at the idea of turning digital designs into solid objects, you’re not alone. 3D printing has skyrocketed from a niche technology to a mainstream marvel that allows anyone to create everything from simple toys to complex machinery parts. So, how exactly does this incredible process work? Let’s break it down from design to creation!
The Design Stage: Where Imagination Meets Reality
At the heart of every 3D printing journey is a design. This is where creativity takes flight! Designers typically use computer-aided design (CAD) software to craft their models. There are many user-friendly options available today, from industry-standard tools to free applications that anyone can download.
The design process is not just about creating appealing visuals; it also involves considerations for how the object will be printed. For instance, most 3D printing technologies layer materials, so the design must support this layering process. Designers must contemplate factors like the object’s stability, strength, and even which way to orient the object during printing for the best outcome.
File Formats: The Language of 3D Printers
Once your design is finalized, it needs to be saved in a format that a 3D printer can understand. The most commonly used file format is STL (stereolithography), which allows for the geometry of the object to be communicated to the printer. Think of STL files as the blueprint that instructs the printer on how to build your creation layer by layer.
That said, there are other formats as well, like OBJ and AMF, which bring their own unique benefits, like supporting color and texture in the case of OBJ. The choice of format often depends on the printer and the complexity of the design.
Slicing the Model: Preparing for Print
Before we hit the print button, there’s an important step that often goes unnoticed: slicing. Slicing software takes your 3D model and breaks it down into hundreds or thousands of horizontal layers. This is crucial because the 3D printer operates by laying down material layer by layer, instead of printing the entire object at once.
The slicing software also allows you to adjust settings like layer height, infill density, and support structures (if your design requires any). For example, you could opt for a high infill density for stronger parts or lower it to save material. It’s a bit like cooking, where changing the ingredients can create different dishes; the right settings can greatly affect the quality and characteristics of your final print.
3D Printing Technologies: Picking Your Method
Now comes the fun part—printing! There are several 3D printing technologies, and the choice often depends on the intended use and the materials involved. Some of the most popular methods include:
-
Fused Deposition Modeling (FDM): This is the most common and accessible method. A thermoplastic filament is heated until it melts, and then it’s extruded through a nozzle to build the object layer by layer. It’s perfect for beginners and hobbyists!
-
Stereolithography (SLA): This method uses a UV laser to cure liquid resin into hardened plastic. SLA typically yields higher precision and detail compared to FDM, making it great for professional applications.
-
Selective Laser Sintering (SLS): SLS works with powdered material. A laser sinters (or fuses) the powder together, layer by layer. It’s often used for functional parts or prototypes.
Post-Processing: The Finishing Touch
Once your 3D print is complete, it usually isn’t ready to showcase just yet. Post-processing is often needed to remove any support structures, refine the surface, and enhance the overall appearance. This can involve sanding, painting, or applying coatings. The extent of post-processing will largely depend on the complexity and purpose of your printed object.
Applications and The Future of 3D Printing
From rapid prototyping in industries to custom jewelry and even medical implants, 3D printing is transforming how we think about manufacturing and design. It’s empowering creators, entrepreneurs, and hobbyists alike to bring their ideas to life on a scale never seen before. As technology advances, we can expect even more exciting applications that may reshape industries and redefine creativity.
So the next time you see a 3D printed object, remember that behind it lies a fascinating journey—from design and slicing to printing and post-processing. This technology isn’t just about making toys or prototypes; it’s about reimagining what’s possible right from our computers into the physical world. It’s a thrilling time to be involved with 3D printing, and who knows what incredible things we’ll create next!